Theme: Fostering Advances, Applications and New Techniques in Clinical Microbiology
Microbiology Meet 2020
Dear Potential Researchers, Scientists, Industrialists & Students,
Join us for 3rd International Conference on Clinical Microbiology, Virology and Infectious Diseases
Update your skills, Meet your academic heroes, Engage in high-level debates and refine your ideas enhance your knowledge base, and broaden your horizons, Visit a new place and have fun, - all in one place!
Date: June 12- 13, 2020
WEBINAR
If you are interested to be a part of this event as a speaker or delegate!
Email: lucywatson@memeetings.net
Call: 1-201-380-5561 (Extension No- 7007)
WhatsApp: +44 7723584505
Microbiology Meet 2020 is the finest opportunity to interact with scientists, researchers, professors, engineers, and directors of various companies, industrial professionals and students in the field of microbiology, virology, infectious diseases and other related fields to share their knowledge. We also take immense pleasure in welcoming various professionals from different countries all over the globe.
Microbiology Meet 2020 is an international platform for establishing research works and therapeutic findings and disorders based on microbial diseases, viruses and infections caused by bacteria, fungi and protists. These types of diseases may be caused due to water borne, food borne, and air borne in human beings as well as in plants and animals. As far as microbiology and virology are concerned, the microbes are considered the root of most of the world's pressing problems. It also represents the increasing importance of human mortality around the globe, thereby vaccination and vaccine development plays an important role in terms of global health.
Target Audience of Microbiology Meet 2020
- Microbiologist
- Virologists
- Parasitologist
- Bacteriologist
- Pharmacists
- Epidemiologists
- Dermatologists
- Neurologist
- Ophthalmologist
- Cardiologist
- Infectious Diseases Researchers, Scientists, Faculties, Students
- Infectious Diseases Associations and Societies
- Directors, Board Members, Presidents, Vice Presidents
- Business Entrepreneurs and Industrialists
- Deans and Head of the Departments
- Medical Colleges, Hospitals & Labs
- Pharmaceutical Companies and Industries
- Medical Devices Manufacturing Companies
- Drug Manufacturing Companies and Industries
- Laboratory Technicians and Diagnostic Companies
1. Microbiology
Microbiology is the scientific study of microorganisms. Microorganisms are those organisms that are too small to see and include things such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses in the naked eye. Microbiology provides the information needed to create vaccines and treatments for diseases. Biologists use microbiology to develop new methods of combating illness. Microbiologists are often employed by companies to develop new products that kill viruses and bacteria.
- Microbes and diseases
- Types of microbiology
- Uses of microbiology
2. Clinical Microbiology
Clinical Microbiology is a branch of medical science which mainly deals with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of infectious diseases. It is concerned about various clinical applications of microbes for the improvement of health. Clinical Microbiology plays an important role in patient care by providing the cause of infection and antimicrobial susceptibility data to physicians. Rapid diagnosis of pathogens is necessary to facilitate the successful administration of antibiotics and to increase treatment rates. It has different methods of analysis used to identify and isolate the microbes.
- Isolation of microbes
- Characterization of microbes
- Clinical trials
- Scope of clinical microbiology
3. Microbes and Infectious Diseases
Not every microbe is harmful to health, but some are helpful in maintaining a healthy digestive system, in daily factories, in bakeries, etc. bring alternations in health and well-being conditions of human beings are termed as pathogens or the harmful ones. Each pathogen has its own activating or residing sites along with its peculiar and individualistic characteristics, sources and symptoms.
Firstly, based on the age category to which they spread infections, they cause
- Pediatric infectious diseases
- Adult infectious diseases
- Secondly, basing on the mode of transmission, they cause:
- Vector borne and zoonotic infectious diseases
- Food and water borne infectious diseases
- Airborne and contact infectious diseases
4. Pediatric Infectious Diseases
Pediatrics is a branch of medicine which deals with and comprises the medical care and treatment of newborns, infants, and children with an age limit from 0-18 i.e. from birth till 18 years of age. Pediatric infectious diseases are diseases that are caused due to pathogens from bacteria, fungi, viruses and other pathogens. These kinds of pathogens infect the well-being of children and make them unhealthy, ill and sick causing several harm and dangers. These infections may lead to Influenza, Cholera, Diarrhea, vomiting tendencies in babies. Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RVS) and Sepsis are very common and contagious form of infections in babies. When the level of infection goes to the extreme, it disturbs babies ' sleeping patterns and food-in-taking ability to project them with pain, discomfort, and trouble.
- Lyme disease
- HIV / AIDS
- Complicated pneumonias
- Osteomyelitis (infection of the bone)
- Tuberculosis
- Persistent fever or fever of unknown origin
- Lymphadenopathy (inflammation of the lymph nodes)
- Recurrent infections
5. Adult Infectious Diseases
Adult infectious diseases are diseases caused by bacterial, fungal, viral and other pathogens that affect adults of 18 years age and older. Such types of viruses affect adults ' health conditions, leaving them unhealthy and ill, resulting in many health hazards and even death. Some of the examples of Adult Infectious Diseases are:
- HIV/AIDS.
- Blood infections.
- Cancer-related infections.
- Hepatitis B and C.
- Human papilloma virus (HPV)
- Staph infections (Staphylococcus aureus infections)
- Antibiotic-resistant infections like MRSA.
- Respiratory infections including flu, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), pneumonia and tuberculosis
6. Airborne and Direct Contact Diseases
Airborne diseases are caused by pathogenic microbes which are small enough and released from an infected person through sneezing, coughing, laughing and close personal contact or microbe aerosolization. The microbes that have been discharged remain suspended on particles of dust, respiratory and water droplets in the air. Illness is caused when the microbe is inhaled or contacts mucus membranes or when secretions remaining on a surface are touched.Contact Diseases are transmitted when an infected person has direct physical contact with an uninfected person and the microbe is transmitted from one person to another. Contact diseases may also spread through indirect contact with the environment or personal items of an infected person. The presence of wound drainage or other body discharges indicates an increased potential for transmission risk and contamination of the environment. Precautions to create a barrier and procedures that reduce or eliminate the microbe in the atmosphere or on personal belongings are the basis for interrupting direct contact disease transmission. Some of the Airborne and Direct contact diseases include:
- Anthrax
- Coronavirus
- Group A streptococcus
- Influenza
- Measles
- Mumps
- Pertussis
- Plague
- Strep pneumoniae
- Tuberculosis
- Varicella
7. Virology
Virology is the study of viruses – submicroscopic, genetic material parasitic particles contained in a protein coat and virus-like agents. This focuses on the following viral aspects: their composition, identification and evolution, infection and exploiting host cells for reproduction, their interaction with the physiology and immunity of the host organism, the diseases they cause, the isolation and cultivation techniques and their use in research and therapy. Virology is considered a sub-field of medicine or microbiology.
- Structure and Classification of Virus
- Viral Diseases and Host Defenses
- Molecular Biology Research and Viral Therapy
8. Human Virology and Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases befall when organisms such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi come into our bodies and make us sick. These sicknesses can be passed from person to person. Hepatitis is a medical condition defined by the liver's tenderness and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the organ's tissue. Hepatitis A is an intense irresistible infection of the liver instigated by the hepatitis A virus. Hepatitis B is a hepatitis B virus (HBV) infectious disease that affects the liver. It can cause infections that are both severe and chronic. HCV is spread mostly by blood-to-blood contact linked with intravenous drug. IHV focuses on the prevention of
- HIV / AIDS
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis B
- Human papilloma virus infection
9. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases
Vector borne and zoonotic diseases (VBZD) are infectious diseases whose transmission involves animal hosts or vectors. Vector borne diseases, such as malaria, are those in which an organism, usually mosquitoes, ticks, or mites, carries a pathogen from one host to another, with the pathogen in the vector generally being more dangerous (virulent). Zoonosis, such as avian flu, is viruses that can be transmitted from animals to humans through animal touch or through vectors that bring zoonotic pathogens from animals to humans. While many VBZD, such as malaria, yellow fever, dengue, and murine typhus, are rarely seen in the United States, we are directly susceptible to VBZD that are found in warmer climates and vulnerable due to global trade and travel. Many VBZD are climate sensitive and ecological shifts associated with climate change are expected to impact the distribution and incidences of these diseases.
- Birld flu
- Swine flu
- Dengue
- Malaria
- Yellow fever
10. Food and Water Borne Diseases
Foodborne disease is a gastrointestinal (GI) tract infection or inflammation caused by food or drink containing harmful bacteria, worms, viruses, or chemicals. Common symptoms of the foodborne disease include nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and chills. Waterborne diseases are caused by microorganisms that are mostly transmitted through contaminated freshwater. Data is available for some water, hygiene-related and sanitation diseases such as cholera, salmonellosis, or shigellosis. Some of common Food and Water borne diseases are:
- Travelers’ diarrhea.
- Giardia and cryptosporidium.
- Dysentery.
- Salmonella.
- Typhoid fever.
- Cholera.
- Hepatitis A
- Norovirus (Norwalk Virus)
- Campylobacter.
- E. coli.
11. Viral Oncology
Oncoviruses are implicated in about 12% of all cancers in humans. At least one of these oncoviruses is harbored by a large number of the world's population, but only a small proportion of these individuals develop cancer. The interplay between host and viral factors is a complex process that works together to create a microenvironment. Oncovirus infections are common, but cancer is rarely caused by these infections. One or more additional insults are required for cancer growth, such as chronic inflammation, environmental mutagens or immunosuppression.
- Human oncoviruses
- Classification of oncoviruses
12. Bacterial and Viral Vaccines
Immunization (vaccination) can be discrete as active immunity formed by vaccine. It is the process of creating tolerance and immunological retention that is consistent with natural infection but deprived of disease risk. There are two rudimentary categories of vaccines: live attenuated and inactivated. Live attenuated vaccines are developed in a research laboratory by altering and modifying the virus or bacterium that causes the disease. Bacterium-derived vaccines are referred to as bacterial vaccines and viral vaccines. The subsequent vaccine retains the ability to duplicate and produce immunity for the body but does not generally cause disease. Inactivated vaccines can be self-possessed either through parts of viruses or bacteria, or throughout either of them.
- Pneumovax 23 (Pro)
- Prevnar 13 (Pro)
- Biothrax (Pro)
- Afluria (Pro)
- Zostavax (Pro)
- Attenuvax
13. Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution in defined populations (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of conditions of health and disease. Disease causation, transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, forensic epidemiology, environmental epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, biomonitoring, screening and comparisons of treatment effects such as clinical studies are the major areas of Epidemiological studies. Many scientific fields such as biology are used by epidemiologists to improve and understand the processes of disease, statistics to use data efficiently and draw appropriate conclusions, social sciences to better understand proximate and distal causes, and exposure assessment engineering.
- Types of epidemiological studies
- Applied field epidemiology
- Epidemiologic characters of infectious diseases
14. Antibiotics/ Antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that destroys or prevents the growth of microorganisms. It is possible to group antimicrobial medicines according to the microorganisms against which they mainly function. Antibiotics are used for bacteria, for example, and antifungals are used for fungi. They can also be classified by their function. Agents which kill microbes are called microbicidal, and those which merely inhibit their growth are called biostatic. The use of antimicrobial medicines to treat infection is known as antimicrobial chemotherapy, while it is known as antimicrobial prophylaxis to use antimicrobial medicines to prevent infection. The main classes of antimicrobial agents are:
- Disinfectants
- Antibiotics
- Role of antibiotics in oculoplastic surgery
- Antiseptics
- Sulfonamides, etc.
15. Rare, Neglected & Tropical Infectious diseases
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) are a miscellaneous collection of tropical contaminations which are particularly common in low-income inhabitants in emerging regions of Africa, Asia, and America. They are instigated by a variety of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa and helminthes. Three major diseases differentiate these diseases, which usually receive better treatment and funding for research. The effect of these diseases as a group is like tuberculosis and malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Co-infection with neglected tropical diseases can also make HIV / AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly.
- Malaria
- Dengue
- Leishmaniasis
- Chagas disease
- African trypanosomiasis
16. Bacterial and Fungal Infectious Diseases
Bacteria are living things with just one cell. These look like spheres, sticks, or spirals under a microscope. They are so tiny that a 1,000 line could fit through a pencil eraser. Some bacteria will not harm you-less than 1% of the various types of bacteria will make people sick. Many of them are supportive. Many bacteria help digest food, kill cells that cause disease, and provide nutrients that the body needs. Also used in the production of healthy foods such as yogurt and cheese. But some bacteria are harmful (Infectious Bacteria) that make you ill. Fungal diseases are often caused by environmentally common fungi. Most fungi are not toxic, but there are some types that can be harmful to health. Mild skin diseases of the fungus may look like a rash and are very common. In the lungs, fungal diseases sometimes mimic other diseases such as flu or tuberculosis. Many fungal diseases, such as fungal meningitis and infections of the bloodstream, are less common than infections of the skin and lung, but can be lethal.
- Diseases caused by bacteria
- Most common bacterial diseases
- Examples of fungal diseases
- Types of fungal diseases
17. Infection and Immune System
Human immune systems are classified into two categories: innate (natural) immunity and adaptive (acquired) immunity. There are major differences between the two divisions, but they share some cell functions and components. All living organisms are subjected to get attacked from disease-causing agents or pathogens. When species become more complex, this mechanism of defense becomes more sophisticated. Multicellular animals have devoted cells or tissues to deal with infection. Other rejoinders are slower but are more adapted to the infecting agent. Jointly, these protections are known as the immune system. The main portions of the immune system are: the natural barriers (skin, mucous membranes, etc.), nonspecific cells (phagocytes, natural killer cells, etc.), and nonspecific molecules (complement, interferon, etc.). Furthermore, the immune system's response to microorganism invasion depends on many factors, such as nutrition, general health, age, and any human host's genetic makeup.
- Innate immune system
- Adaptive immune system
18. Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases
Many infectious diseases have similar signs and symptoms. Your body fluid tests will usually reveal signs of the underlying mistake that triggers your health problem. It helps to tailor the treatment to your doctor. Through sticking a needle into a vein, usually in your neck, a technician gets a sample of your blood. This painless take a look at needs you to urinate into instrumentality. You will be tutored to clean up the reproductive organ area with associate in nursing antiseptic pad and collect the wee-wee center to avoid potential contamination of the specimen. You could also take samples from your throat or other wet areas of your body with a sterile swab. As a result, a research laboratory will scan the specimen for parasites and alternative species. This technique gives a snapshot of your mood through a fastidiously positioned needle between your lower spine's bones. Typically, together with your knees, you may be asked to lie on your face forcing up to your chest.
- Symptomatic diagnosis
- Microscopy
- Biochemical tests
- PCR- based diagnostics
- Meta genomic sequencing
- Symptomatic diagnosis
19. Microbial Vaccines and Advancements
A vaccine is a type of microorganism or virus that is injected into the body to induce real infection. Due to the fact the vaccinated microbes are 'dead,' they do not motive a person to end up sick. Relatively speaking, vaccines promote and improve immune response by properly using the body to fight all kinds of infections. It sums up infectious disease objectives and non-infectious ailment targets. To produce vaccine-mediated defense is a multifaceted mission. The vaccines are generally well developed and empirically more effective, with less or no knowledge on how to set off the immune system. Their early defensive efficacy is usually consulted via the induction of antigen-particular antibodies. However, there's more to antibody-mediated protection than the peak of vaccine-prompted antibody titers.
- Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Vaccine
- Polio Vaccines
- Diphtheria/Tetanus/Pertussis (DTP) Vaccines
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
- Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines (PCVs)
20. Medical, Clinical and Diagnostic Virology
Clinical or medical specialization is that the field of additional medicines deals specifically with the clinical manifestations of pathology consisting of the isolation of 1 or additional viruses to blame direct or indirect methodologies such as cell culture, serology, organic chemistry and biology for human pathogens. Basically, due to the sub-field of drug biology, a medical specialty is considered. In practice, the diagnostic medical specialty is now becoming a thought. There are various ways for the laboratory classification of infections of microorganisms that have a culture of microorganisms, identification of matter, detection of macro-molecules in the designation of medical specialty. Moreover, it's the same that diagnostic medical specialty has modified apace because of molecular techniques and clinical sensitivity of medical science assays.
- Methods used in diagnostic virology
- Antiviral susceptibility testing
21. Prevention, Control and Treatment of Infectious Diseases
Prevention and control of infections (IPC) is a scientific approach and practical solution designed to prevent patients and health workers from harm caused by infection. It is focused on infectious diseases, epidemiology, social science and the health system. IPC holds a unique position in the field of patient safety and high-quality universal healthcare coverage as it is important to health workers and patients at each healthcare conference.
- Hand hygiene
- Prevention of surgical site infections
- IPC to combat antimicrobial resistance
- Injection safety
- Burden of health care-associated infections
- Ebola response and recovery
- IPC country capacity-building
- Prevention of bloodstream infections
- Prevention of urinary tract infections.
21. Novel Coronavirus (Covid-19)
Covid-19 or coronavirus is a novel virus with high affinity to spread in the community In December 2019, it was first identified in Wuhan, China The symptoms are non-specific, so fever, cough, dyspnea, are prominent features Respiratory failure and mortality have also been reported.
Maximum people infected with the COVID-19 virus will experience temperate to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment. Older people and those with elemental medical problems like diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, cardiovascular disease and cancer are more likely to develop serious illness.
The best way to avert and slow down transmission is be well informed about the COVID-19 virus, the disease it causes and how it spreads. Protect yourself and others from infection by washing your hands or using an alcohol-based sanitizers rub frequently and not touching your face.
The COVID-19 virus spreads generally discharge from the nose or through droplets of saliva when an affected person coughs or sneezes, so it’s necessary that you also practice respiratory manners for example, by coughing into a flexed elbow. At this time, there are no particular vaccines or treatments for COVID-19.
Symptoms of Coronavirus:
- Fever
- Tiredness
- Dry Cough
Few people may also experience:
- Nasal Congestion
- Runny Nose
- Sore Throat
- Aches and Pains
Market Analysis of Microbiology Conference 2020
Microbiology and Virology including other infectious diseases have become increasingly imperative to human society.it has aroused as one of the most important branches of life science. The disease-causing microbes nearly have an effect on all the active region of our body and therefore produce a good impact towards one’s life.
The field of microbiology has made successive progressions in all fields in less time to improve the quality of life. New medicine, recombinant DNA technology and the production of the latest types of wines and liquors through biology have almost dominated infectious diseases. There is a wide range of scope in the field of microbiology due to its advancements in life science. The scope and benefit in this field and research thanks the contribution and participation of biology in several fields like dairy, medication, pharmacy, industry, clinical research, water industry, agriculture, nanotechnology, and chemical technology. There is an increase in a mandate for clinical microbiologists universally. A life scientist will launch new kits for diagnosis, discover new medicine, teach, research, etc.
Global Microbiology Testing Analysis Market Report:
The global clinical microbiology market was valued at $3.63 billion in the year 2018 and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% to reach $5.23 billion in 2024. The market for microbiology testing is evaluated in instruments and reagents. In 2018, the instruments product section accounted for the biggest share of the market; but, the reagents product section is predicted to grow at a better rate throughout the forecast amount. The biology testing market is segmental into hospitals and diagnostic centers, custom laboratory service suppliers and tutorial and analysis institutes. The key factors driving the expansion of this market embody in progress technological advancements within the field of infectious diseases diagnosing, rising incidence of infectious diseases and growth irruption of epidemics and increased funding and public-private investments for research and innovation.
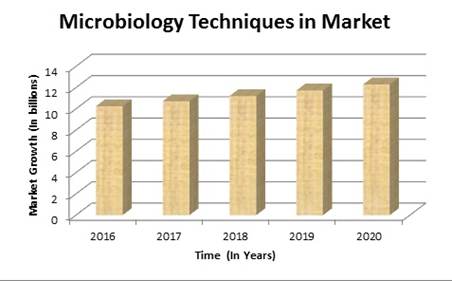
Jun 11, 2019 (The Express wire via COMTEX) -- Microbiology Testing Market Industry 2019 Global Market Research Report 2019 According to the details of the consumption figures, the global Microbiology Testing market is predicted to succeed in the worth of US$ XX million at the top of 2024. Furthermore, Market size, the revenue shares {of each| of every} {segment| phase| section} and its sub-segments, as well as forecast figures are also covered in this report.
World {microbiology science} Monitoring industry study on the major regional business conditions in the world { is a could be a}{professional } and in-depth report { research }focusing on the major regions (North America, Asia-Pacific and Europe). It covers the market landscape and its growth prospects over {the coming| the approaching} years. The report {also| additionally| conjointly} includes a discussion of the Key Vendors {operating| operational| in operation| operative} {in this| during this} {global| international| world} market.
Vaccine Market Report:
Compare to the pharmaceutical market, the vaccine market id relatively small and concentrated on both the supply and demand sides. It is highly regulated and largely dependent on the public purchase and donor policies. The immunogen market has terribly distinct options that increase the quality of assessing and understanding evaluation and acquisition. It is made up of individual markets for individual vaccines or vaccine type, each with their own specificities, particularly on the supply side. The global vaccine market was valued at over $32.5 billion in 2015 and is expected to reach over $77.8 billion by 2024, at a CAGR of 10.3%.
Global Antibiotics Market:
An antibiotic is a chemical compound that kills or slows down the growth of any diseases causing micro-organisms such as bacteria, parasite, and fungi, but is not effective against viruses and prions. Antibiotics act via various mechanisms such as the inhibition of cell wall synthesis, the inhibition nucleic acid synthesis, the disruption of cell membrane, and the inhibition of protein synthesis. The global antibiotics market generated $42.33 billion in 2017 and is expected to reach $49.93 billion by 2025, registering a CAGR of 2.1% from 2018 to 2025. The report covers the current state of affairs and also the growth prospects of worldwide antibiotics marketplace for 2017-2025. The report presents a detailed picture of market by way of study, synthesis and summation of data from multiple sources.
Industrial Microbiology Market:
Industrial Microbiological science is that the application of biological science technique for management and exploitation of microorganisms for production and process of helpful merchandise on a billboard scale. Industrial microbiology has wide applications in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, agriculture products, industrial chemicals, environment and other. The global industrial microbiology market is estimated to be valued at $ 8,878.2 million by 2016 and projected to grow at CAGR of 7.1% to reach $16,455.0 by 2026 end.
Related Microbiology Associations and Societies:
- Federation of American Societies for experimental biology
- Society for Industrial Microbiology and biotechnology
- Society for Applied Microbiology
- International Union of microbiological societies,
- Southern California Branch of the American Society for Microbiology, ,
- Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research,
- Federation of Asia-Pacific Microbiology Societies
- Asia Pacific Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infection
- Federation of European Microbiological Societies
- Malaysian Society of Infectious Diseases,
- Southeastern Association for clinical microbiology,
- Association of medical school microbiology and immunology chairs
- Association for Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
- The American Association of Immunologists
- Association of medical school microbiology and immunology chairs
- British Association of Dermatologists
- European Biosafety Association
- Scottish Microbiology Association
- Association of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Disease Canada
- The Association for Clinical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.
- Harvard University
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- University of Melbourne
- University of California--San Francisco
- University of Oxford
- University of Washington
- Stanford University
- Duke University
- University of Cambridge
- Rockefeller University
- Johns Hopkins University
- Lausanne University Hospital, Switzerland
- University of Tokyo Hospital, Japan
- Massachusetts general Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, New Eastern England, US
- Charité - Berlin University of Medicine, Berlin, Germany
- Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland, US
- Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
- Cleveland Clinic, USA
- Mayo Clinic
- El Camino Hospital – Mountain View, California
Conference Highlights
- Microbiology
- Clinical Microbiology
- Microbes and Infectious Diseases
- Pediatric Infectious Diseases
- Adult Infectious Diseases
- Airborne and Direct Contact Diseases
- Human Virology and Infectious Diseases
- Vector Borne and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases
- Food and Water Borne Diseases
- Viral Oncology
- Bacterial and Viral Vaccines
- Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases
- Antibiotics/ Antimicrobial
- Rare, Neglected & Tropical Infectious diseases
- Bacterial and Fungal Infectious Diseases
- Infection and Immune System
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases
- Microbial Vaccines and Advancements
- Medical, Clinical and Diagnostic Virology
- Prevention, Control and Treatment of Infectious Diseases
- Virology
- Novel Coronavirus (Covid-19)
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 12-13, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Medical Microbiology & Diagnosis
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy
- Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medicine
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by












